低配卖票很多问题 - 进程资源的抢占
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int tickets = 100;
void *sellticket(void *arg) {
while(tickets > 0) {
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets--);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
|
线程同步
线程的主要优势在于,能够通过全局变量来共享信息。不过,这种便捷的共享是有代价的:必须确保多个线程不会同时修改同一变量,或者某一线程不会读取正在由其他线程 修改的变量。
临界区是指访问某一共享资源的代码片段,并且这段代码的执行应为原子操作,也就是 同时访问同一共享资源的其他线程不应终端该片段的执行。
线程同步:即当有一个线程在对内存进行操作时,其他线程都不可以对这个内存地址进 行操作,直到该线程完成操作,其他线程才能对该内存地址进行操作,而其他线程则处 于等待状态。
互斥锁(互斥量)
为避免线程更新共享变量时出现问题,可以使用互斥量(mutex 是 mutual exclusion 的缩写)来确保同时仅有一个线程可以访问某项共享资源。可以使用互斥量来保证对任意共 享资源的原子访问。
互斥量有两种状态:已锁定(locked)和未锁定(unlocked)。任何时候,至多只有一个线程可以锁定该互斥量。试图对已经锁定的某一互斥量再次加锁,将可能阻塞线程或者报 错失败,具体取决于加锁时使用的方法。
一旦线程锁定互斥量,随即成为该互斥量的所有者,只有所有者才能给互斥量解锁。一般情 况下,对每一共享资源(可能由多个相关变量组成)会使用不同的互斥量,每一线程在访问 同一资源时将采用如下协议:
- 针对共享资源锁定互斥量
- 访问共享资源
- 对互斥量解锁
如果多个线程试图执行这一块代码(一个临界区),事实上只有一个线程能够持有该互斥量(其他线程将遭到阻塞),即同时只有一个线程能够进入这段代码区域,如下图所示:
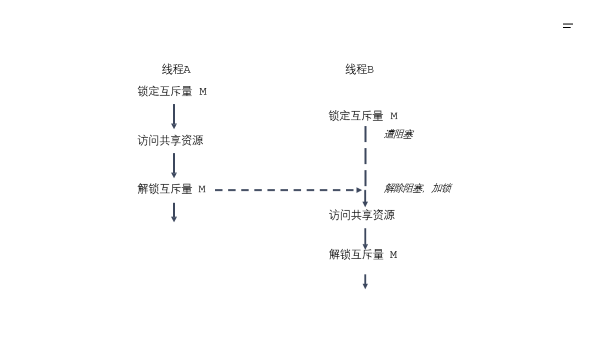
互斥量(互斥锁)相关操作函数及介绍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| 互斥量的类型 pthread_mutex_t
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
- 功能: 初始化互斥量
- 参数:
- mutex: 需要初始话的互斥量变量
- attr: 互斥量相关的属性NULL
- restrict: c语言的修饰符,被修饰的指针,不能由另外的一个指针进行 操作
pthread_mutex_t *restrict = mutex = xxx;
pthread_mutex_t *mutex1 = mutex;
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 功能: 释放互斥量资源
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 功能: 加锁 - 阻塞,如有有一个线程加锁了那么其他线程只能阻塞等待
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 功能: 尝试加锁,如果加锁失败,不会阻塞,会直接返回
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 释放锁(解锁)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int tickets = 1000;
void *sellticket(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(tickets > 0) {
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets--);
} else {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
pthread_exit(NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
|
死锁


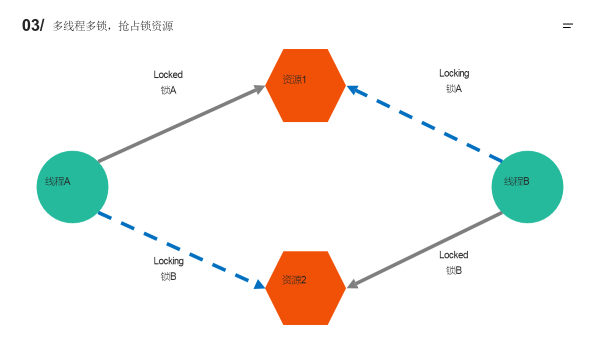
忘记加锁 - 可替换上述函数代码 尝试运行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| void *sellticket(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(tickets > 0) {
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets--);
} else {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
|
重复加锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| void *sellticket(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(tickets > 0) {
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets--);
} else {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
|
多线程多锁,抢占锁资源 - C
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex1, mutex2;
void *workA(void *arg) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
printf("workA\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
return NULL;
}
void *workB(void *arg) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
printf("workB\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex2, NULL);
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, workA, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, workB, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex2);
return 0;
}
|
读写锁
当有一个线程已经持有互斥锁时,互斥锁将所有试图进入临界区的线程都阻塞住。但是考虑一种情形,当前持有互斥锁的线程只是要读访问共享资源,而同时有其它几个线程也想 读取这个共享资源,但是由于互斥锁的排它性,所有其它线程都无法获取锁,也就无法读 访问共享资源了,但是实际上多个线程同时读访问共享资源并不会导致问题。
在对数据的读写操作中,更多的是读操作,写操作较少,例如对数据库数据的读写应用。为了满足当前能够允许多个读出,但只允许一个写入的需求,线程提供了读写锁来实现。
读写锁的特点:
- 如果有其它线程读数据,则允许其它线程执行读操作,但不允许写操作。
- 如果有其它线程写数据,则其它线程都不允许读、写操作。
- 写是独占的,写的优先级高。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| 读写锁的类型 pthread_rwlock_t
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);
- 功能: 初始化读写锁
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 销毁
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 加读锁
int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 尝试加读锁
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 写锁
int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 尝试加写锁
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 功能: 关闭写
|
读写锁(案例) - C
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int num = 1;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
void *readNum(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
printf("==read, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
void *writeNum(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
num++;
printf("++write, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
pthread_t wtids[3], rtids[5];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pthread_create(&wtids[i], NULL, writeNum, NULL);
pthread_detach(wtids[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_create(&rtids[i], NULL, readNum, NULL);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
return 0;
}
|
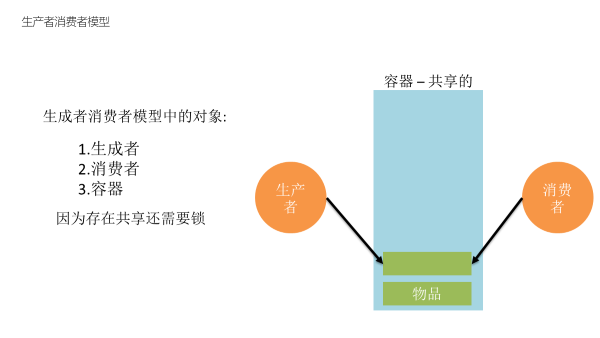
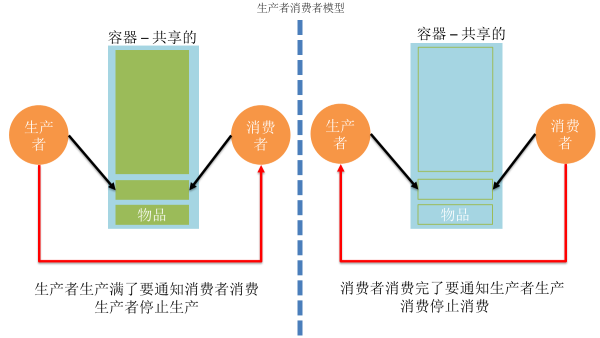
生产者消费者模型
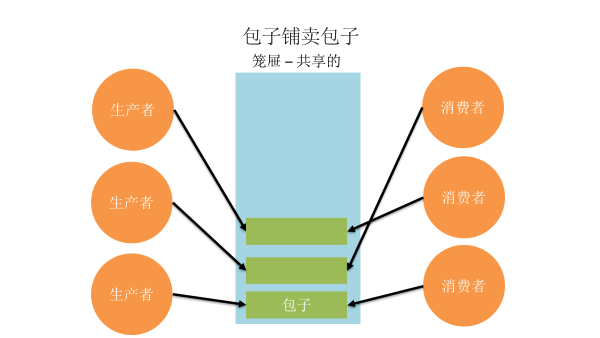
条件变量
条件变量函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| 条件变量的类型 pthread_cond_t
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
- 功能: 初始化
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 功能: 释放
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,thread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
- 功能: 等待,阻塞函数调用了该函数线程会阻塞
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
- 功能: 等待多长时间,调用了这个函数,线程会阻塞,直到指定的时间结束
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 功能: 唤醒一个或者多个等待的线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 功能: 唤醒所以的等待的线程
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
typedef struct Node {
int num;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
struct Node *head = NULL;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void *producer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->num = rand() % 1000;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
void *customer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(head != NULL) {
Node *temp = head;
head = head->next;
printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", temp->num, pthread_self());
free(temp);
} else {
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5];
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_detach(ptids[i]);
pthread_detach(ctids[i]);
}
while(1) {
sleep(10);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
|
信号量
信号量函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| 信号量的类型 sem_t
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
- 功能: 初始化信号量
- 参数:
- sem: 信号量的的地址
- pshared: 0用在线程间、非0用在进程间
- value: 信号量中的值
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
- 功能: 释放资源
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
- 功能: 对信号量加锁,对这个信号量的值减1,如果值为0,就阻塞
int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);
- 功能: 尝试
int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
- 功能: 等待多长的时间
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
- 功能: 对信号量解锁,调用一次对信号的值加1
int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval);
- 功能: 获取
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
typedef struct Node {
int num;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
struct Node *head = NULL;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
sem_t psem;
sem_t csem;
void *producer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
sem_wait(&psem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->num = rand() % 1000;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sem_post(&csem);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
void *customer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
sem_wait(&csem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(head != NULL) {
Node *temp = head;
head = head->next;
printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", temp->num, pthread_self());
free(temp);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sem_post(&psem);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
sem_init(&psem, 0, 8);
sem_init(&csem, 0, 0);
pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5];
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_detach(ptids[i]);
pthread_detach(ctids[i]);
}
while(1) {
sleep(10);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
|

















