类型与变量
类型
变量
最小位数
int
a
16
long long
b
64
char
c
8
double
d
N/A
float
e
N/A
1 2 3 4 5 int a;long long b;char c;double d;float e;
$$
类与对象 $$
什么是面向对象?
面向对象是一种编程思想, 把一切东西看出一个个对象,比如人、耳机、鼠标、水杯等… …他们各自都有属性,比如耳机是白色的,鼠标是黑色的等等,把这些对象拥有的属性变量和操作这些属性的函数打包成一个类来表示
面向过程和面向对象的区别
面向过程: 根据业务逻辑从上到下写代码。
面向对象: 将数据与函数绑定到一起,进行封装, 这样能够更快速的开发程序,减少了重复代码的重写过程
类(类型)
对象(变量)
Cat
garfield
Dog
odie
People
qz
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Cat {}; class Dog {}; class People {};
1 2 3 Cat garfield; Dog odie; People qz;
成员属性方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class People { string name; Day birthday; double height; double weight; void say (string word) void run (Location &Ioc) };
访问权限 数据安全性
名
描述
public
公共访问权限
private
私有访问权限
protected
受保护的访问权限
friend
友元
访问权限就相当于类外 对访问类内 部的属性和方法的时候才起到作用
public : 类外部可以随意访问的
private : 类外部是访问不了的
protected : 只有子类才能访问的
friend :隔壁老王
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class People { public : string name () string birthdat () double heig private : };
命名空间 命名空间可以:
命名空间的定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;namespace ttw { int a, b; } namespace qz { int a, b; } int main () ttw::a = ttw::b = 1 ; qz::a = qz::b = 2 ; cout << ttw::a << qz::a << endl ; return 0 ; }
去掉 using namespace ***; 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> using namespace ttw;namespace ttw { int a, b; } namespace qz { int a, b; } int main () a = b = 1 ; qz::a = qz::b = 2 ; cout << a << qz::a << endl ; return 0 ; }
命名空间嵌套 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <iostream> using namespace ttw;namespace ttw { int a = 1 ; namespace qz { int a = 2 ; } } int main () cout <<"ttw 中的 a : " << ttw::a << endl ; cout <<"q z 中的 a : " << ttw::qz::a << endl ; return 0 ; }
命名空间是开放的,既可以随时把新的成员加入已有的命名空间中(向命名空间中追加) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> using namespace ttw;namespace ttw { int a = 1 ; } namespace ttw { int b = 2 ; } int main () cout << ttw::a << endl ; cout << ttw::b << endl ; return 0 ; }
类 先构造后析构, 不仅作用在成员属性之间也作用在类之间
类-代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;#define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(TEST1) class A_with_int { int a; double b; void say () }; class People {public : string name; int age; double height; double weight; void say (string name) void run () }; ENDS(TEST1) void TEST1::People::say(string name) { cout << "my first name is" << this ->name << endl ; cout << "my second name is " << name << endl ; return ; } int main () cout << "class A int " << sizeof (TEST1::A_with_int) << endl ; TEST1::People ttw; TEST1::People laojia; TEST1::People jgouba; TEST1::People jdp; ttw.name = "Tu tou wang" ; laojia.name = "Lao jia" ; jgouba.name = "Jia gou ba" ; jdp.name = "Jia da pao" ; ttw.say("TTW" ); laojia.say("LJ" ); jgouba.say("JGB" ); jdp.say("JDP" ); return 0 ; }
类对象的 大小问题
相关类型在数据区中的存储空间
因为方法区的大小不会随着对象的曾加而增加
sizeof() 只计算和对象数量成正比的数据区的大小
实现自己的cout、cin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include <iostream> #define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(ttw) class istream {public : istream &operator >>(int &x); }; istream &istream::operator >>(int &x) { scanf ("%d" , &x); return *this ; } istream cin ; class ostream {public : ostream &operator <<(int x); ostream &operator <<(char ch); }; ostream &ostream::operator <<(int x) { printf ("%d" ,x); return *this ; } ostream &ostream::operator <<(char ch) { printf ("%c" , ch); return *this ; } ostream cout ; const char endl = '\n' ;ENDS(ttw) int main () int n = 123 ; std ::cout << n << std ::endl ; ttw::cout << n << ttw::endl ; ttw::cin >> n; ttw::cout << n << ttw::endl ; return 0 ; }
为什么重载左移运算符要返回引用?
是为了连续输出
比如 1 + 2 + 3 + 5
先 1 + 2 = 3
3(用的是1 + 2的结果的返回值) + 3
这是为了实现连续加
// cout(左面的参数) << p(右面的参数)
引用-代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;void add_one (int &n) n += 1 ; return ; } int main () int a = 1 , b = 3 ; cout << "normal param : " << a << " " << b << endl ; add_one(a); add_one(b); return 0 ; }
构造函数与析构函数
构造/析构函数
使用方法
默认构造函数
People a;
People(string name);
People(“ttw”);
People(consst People &a)
拷贝构造,与=不等价
~People
无
任何一个对象产生的时候都会调用构造函数,销毁的时候一定会调用析构函数
构造函数有参数:
一个参数: 通常叫转换构造
多个参数:
构造函数—代码实现 在类里面编译器会几类默认的行为:
默认构造函数
默认析构函数
默认拷贝构造
默认复制运算符
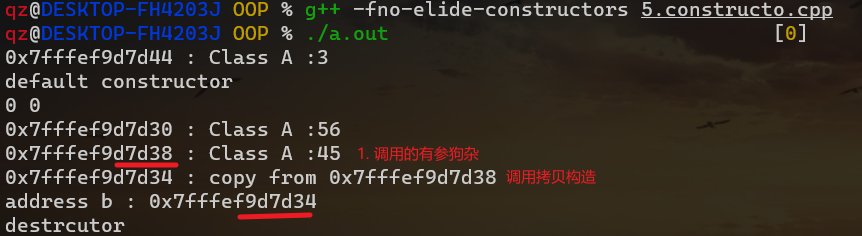
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class B1 {public : B1() = default ; B1(const B1 &) { cout << "B1 copy constructor" << endl ; } }; class B2 {public : B2() = default ; B2(const B2 &) { cout << "B2 copy constructor" << endl ; } }; class B3 {public : B3() = default ; B3(const B3 &) { cout << "B3 copy constructor" << endl ; } }; class B {public : B1 b1; B2 b2; B3 b3; }; class A {public : A(int x) : x(x) { cout << this << " : Class A :" << x << endl ; } A(const A &a) { cout << this << " : copy from " << &a << endl ; } void operator =(const A &a) { cout << this << " assign from " << &a << endl ; } int x; }; class Data {public : Data() : __x(0 ), __y(0 ), a(3 ) { cout << "default constructor" << endl ; } int x () return __x ;} int y () return __y; } ~Data() { cout << "destrcutor" << endl ; } private : int __x, __y; A a; }; int main () B b1; B b2 = b1; Data d; cout << d.x() << " " << d.y() << endl ; A a (56 ) ; A b = 45 ; cout << "address b : " << &b << endl ; b = 78 ; return 0 ; }
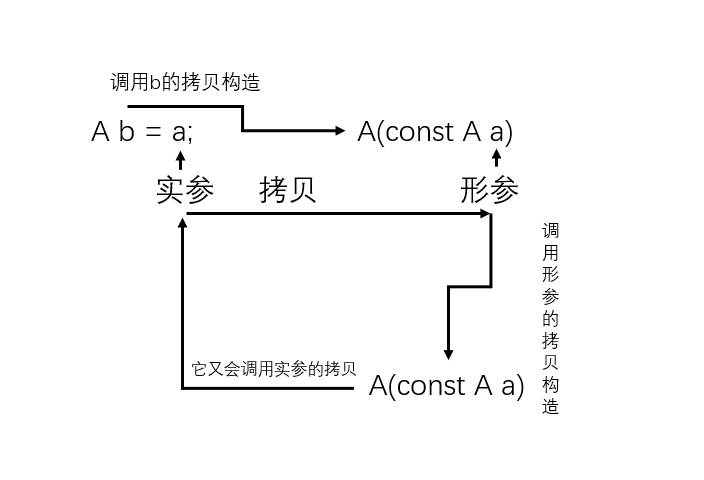
为什么拷贝构造要传引用?不加行不行?
拷贝构造为什么不能去掉const? int & 是不能绑定到匿名对象身上的
两点为什么要加:
加上const为了兼容匿名对象
逻辑上的常量限制
兼容const类型的拷贝
const A a(45);
A b = a;
拷贝执行流程 为什么多一个相当于 45 创建了一共匿名对象
取消返回值优化 1 g++ -fno-elide-constructors test.cpp
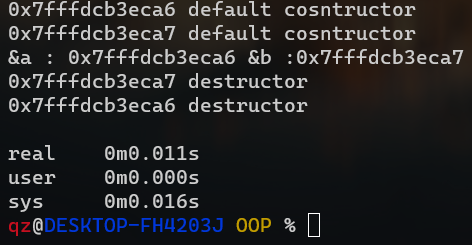
析构函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class A {public : A() { cout << this << " default cosntructor" << endl ; } A(int n, int m) : n(n), m(m), arr(nullptr ), size(nullptr ), offset(nullptr ) { cout << "A(int) constructor" << endl ; } A(int *size, int *offset) : size(size), offset(offset) { arr = new int [*size]; arr += *offset; cout << "A(int *size) constructor" << endl ; } ~A() { cout << this << " destructor" << endl ; if (arr == nullptr ) return ; arr -= *offset; delete []arr; arr = nullptr ; } int *arr, *size, *offset ; int n, m; }; int main () A a (3 , 4 ) ; A b (&a.n, &a.m) ; cout << "&a : " << &a << " &b :" << &b << endl ; return 0 ; }
构造函数与析构函数顺序相反是特例么?还是一般情况?
一定是一般情况。
a对象定义在b前面,意味着b构造可能依赖于a对象,所以a一定先构造
析构-代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;#define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(test1) class A {public : A() { cout << this << " default cosntructor" << endl ; } A(int n, int m) : n(n), m(m), arr(nullptr ), size(nullptr ), offset(nullptr ) { cout << "A(int) constructor" << endl ; } A(int *size, int *offset) : size(size), offset(offset) { arr = new int [*size]; arr += *offset; cout << "A(int *size) constructor" << endl ; } ~A() { cout << this << " destructor" << endl ; if (arr == nullptr ) return ; arr -= *offset; delete []arr; arr = nullptr ; } int *arr, *size, *offset ; int n, m; }; void main () A a (3 , 4 ) ; A b (&a.n, &a.m) ; cout << "&a : " << &a << " &b :" << &b << endl ; return ; } ENDS(test1); BEGINS(test2) #define ATTR_CLASS(x) class ATTR_##x {\ public :\ ATTR_##x() { \ cout << "ATTR_" #x " default constructor" << endl; \ } \ ~ATTR_##x() { \ cout << "ATTR_" #x "destructor" << endl;\ }\ }; ATTR_CLASS(1 ); ATTR_CLASS(2 ); ATTR_CLASS(3 ); ATTR_CLASS(4 ); class A {public : A() { cout << "Class A constructor" << endl ; } ~A() { cout << "Class A destructor" << endl ; } ATTR_1 a1; ATTR_2 a2; ATTR_3 a3; ATTR_4 a4; }; void main () A a; return ; } ENDS(test2) int main () test1::main(); cout << " ------------------------------------ " << endl ; test2::main(); return 0 ; }
类属性与方法 如果把成员属性变成类属性?
在属性前面添加static关键字即可
他们主要是性质上的差别,就导致上了功能上的差别
非对象行为:
列如:毁灭全人类
不能访问this指针 (相当于非对象方法)
成员方法
对象行为:
列如:人类
说话、跑、
他们主要的差别是逻辑上的差别
很多功能我们可以设计成类方法或者是成员方法,主要是看相应方法的内部使不使用this指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class People {public : static void is_valid_height (double height) private : static int total_num; double __height; };
const方法 const 放到方法后面
1 2 3 4 class People { public : string &name () const };
const对象只能调用const方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;#define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(test1) class A {public : A() { x = 200 ; } void say () const x = 123 ; cout << x << endl ; } mutable int x; }; void main () const A a; a.say(); return ; } ENDS(test1); int main () test1::main(); return 0 ; }
C++中的结构体与类
struct 访问权限默认 public
class 访问权限默认 private
c/c++结构体的区别
C
C++
成员函数
不能有
可以
静态成员
不能有
可以
访问控制
默认public,不能修改
public/private/protected
继承关系
不可以继承
可以从类或者其他结构体继承
初始化
不能直接初始化数据成员
可以
为什么C++还会保留struct关键字更好的兼容
用严格准确的逻辑, 将错误暴露在编译阶段
C++ 核心精髓:不仅要说话,还要说的漂亮话
浅拷贝与深拷贝
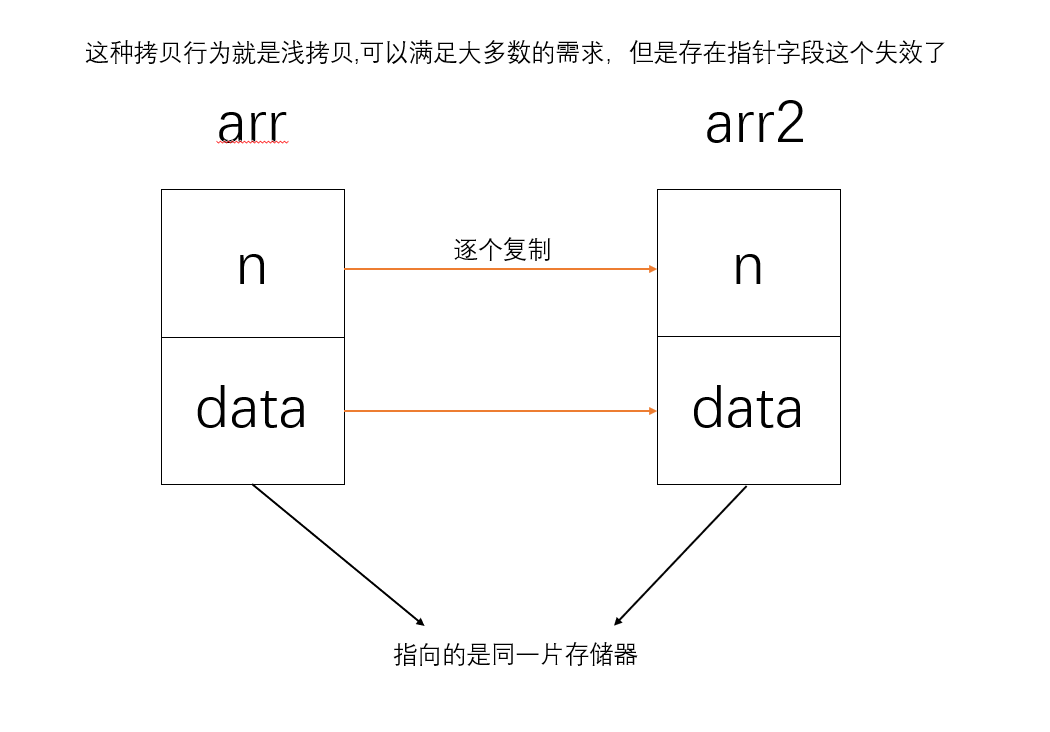
浅拷贝:
又称值拷贝,将原对象的值拷贝到目标对象中去,本质上来说源对象和目标对象公用一份实体,只是所引用的变量名不同,地址其实还是相同的。举个简单的例子,你的小名字叫嘻嘻,大名叫哈哈,当别人叫你嘻嘻或者哈哈的时候你都会应答,这个两个名字虽然不同,但是都指的是你
深拷贝:
拷贝的时候先开辟出和源对象大小一样的空间,然后将源对象里的内容拷贝到目标对象中去,这样两个指针就指向了不同的内存位置。并且里面的内容是一样的,这样不但达到了我们想要的目的,还不会出现问题,两个指针先后调用析构函数,分别释放自己所指向的位置,即为每次增加一个指针,便申请一块新的内存,并让这个指针指向新的内存,深拷贝情况下,不会出现重复释放同一块内存的错误
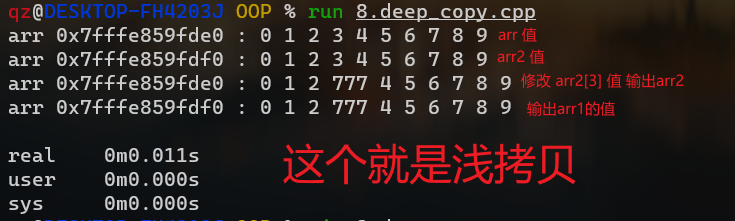
浅拷贝 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class Vector {public : Vector(int n = 100 ) : n(n), data(new int [n]) {} int &at (int ind) return data[ind]; } int &operator [](int ind) { return data[ind]; } void output (int m = -1 ) if (m == -1 ) m = n; cout << "arr " << this << " : " ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) { cout << data[i] << " " ; } cout << endl ; return ; } private : int n; int *data; }; int main () Vector arr; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arr[i] = i; } arr.output(10 ); Vector arr2 (arr) ; arr2.output(10 ); arr2[3 ] = 777 ; arr.output(10 ); arr2.output(10 ); return 0 ; }
正常是思维:我想把arr拷贝给arr2, arr2是应该不影响arr1的
问题就处在默认的拷贝行为
深拷贝
深拷贝使用 memcpy 是不对的,因为数据存储区也需要深拷贝时候
memcpy(data, a.data, sizeof(int) * n);
贴个有错误的代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std ;#define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(ttw) class A {public : int x, y; }; ostream &operator <<(ostream &out, const A &a) { out << "(" << a.x << "," << a.y << ")" ; return out; } template <typename T>class Vector {public : Vector(int n = 100 ) : n(n), data(new T[n]) {} Vector(const Vector &a) : n(a.n) { data = new T[n]; memcpy (data, a.data, sizeof (T) * n); return ; } T &at (int ind) { return data[ind]; } T &operator [](int ind) { return data[ind]; } void output (int m = -1 ) if (m == -1 ) m = n; cout << "arr " << this << " : " ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { cout << data[i] << " " ; } cout << endl ; return ; } private : int n; T *data; }; ENDS(ttw) BEGINS(test1) int main () ttw::Vector<int > arr1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arr1[i] = i; } arr1.output(10 ); ttw::Vector<int > arr2 (arr1) ; arr2.output(10 ); arr2[3 ] = 777 ; arr1.output(10 ); arr2.output(10 ); return 0 ; } ENDS(test1) BEGINS(test2) using namespace ttw;int main () Vector<A> arr1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arr1[i].x = i; arr1[i].y = 2 * i; } arr1.output(10 ); Vector<A> arr2 (arr1) ; arr2[3 ] = (A){4 , 1000 }; arr1.output(10 ); arr2.output(10 ); return 0 ; } ENDS(test2) BEGINS(test3) using namespace ttw;int main () Vector<Vector<int >> arr1; Vector<Vector<int >> arr2(arr1); arr2[2 ][2 ] = 100 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { arr1[i].output(3 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { arr2[i].output(3 ); } return 0 ; } ENDS(test3) int main () test1::main(); cout << " ------------------------------ " << endl ; test2::main(); cout << " ------------------------------ " << endl ; test3::main(); return 0 ; }
贴一个无错误的 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std ;#define BEGINS(x) namespace x { #define ENDS(x) } BEGINS(ttw) class A {public : int x, y; }; ostream &operator <<(ostream &out, const A &a) { out << "(" << a.x << "," << a.y << ")" ; return out; } template <typename T>class Vector {public : Vector(int n = 100 ) : n(n), data((T *)calloc (sizeof (T), n)) {} Vector(const Vector &a) : n(a.n) { data = (T *)malloc (sizeof (T) * n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { new (data + i) T(a.data[i]); } return ; } T &at (int ind) { return data[ind]; } T &operator [](int ind) { return data[ind]; } void output (int m = -1 ) if (data == nullptr ) return ; if (m == -1 ) m = n; cout << "arr " << this << " : " ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { cout << data[i] << " " ; } cout << endl ; return ; } private : int n; T *data; }; ENDS(ttw) BEGINS(test1) int main () ttw::Vector<int > arr1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arr1[i] = i; } arr1.output(10 ); ttw::Vector<int > arr2 (arr1) ; arr2.output(10 ); arr2[3 ] = 777 ; arr1.output(10 ); arr2.output(10 ); return 0 ; } ENDS(test1) BEGINS(test2) using namespace ttw;int main () Vector<A> arr1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arr1[i].x = i; arr1[i].y = 2 * i; } arr1.output(10 ); Vector<A> arr2 (arr1) ; arr2[3 ] = (A){4 , 1000 }; arr1.output(10 ); arr2.output(10 ); return 0 ; } ENDS(test2) BEGINS(test3) using namespace ttw;int main () Vector<Vector<int >> arr1; Vector<Vector<int >> arr2(arr1); arr2[2 ][2 ] = 100 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { arr1[i].output(3 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { arr2[i].output(3 ); } return 0 ; } ENDS(test3) int main () test1::main(); cout << " ------------------------------ " << endl ; test2::main(); cout << " ------------------------------ " << endl ; test3::main(); return 0 ; }
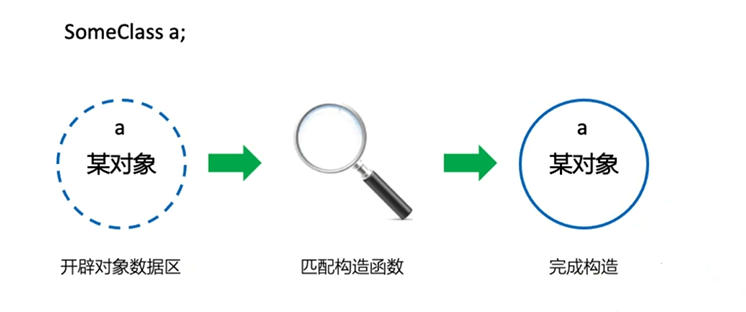
返回值优化(RVO) 对象的初始化 什么是我们认为内存中完整的对象?
那就是经历了构造过程的数据存储区
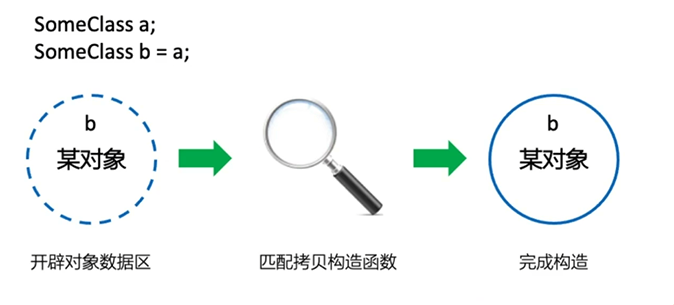
拷贝构造
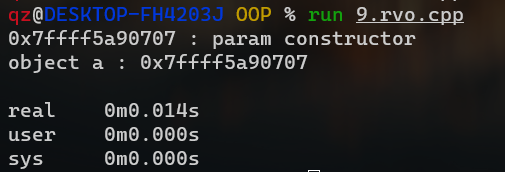
返回值优化 (RVO) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class A {public : A() { cout << this << " : default constructor" << endl ; } A(int x) { cout << this << " : param constructor" << endl ; } A(const A &a) { cout << this << " : copy constructor" << endl ; } }; A func () { A temp (3 ) ; cout << "object temp : " << &temp << endl ; return temp; } int main () A a = func(); cout << "object a : " << &a << endl ; return 0 ; }
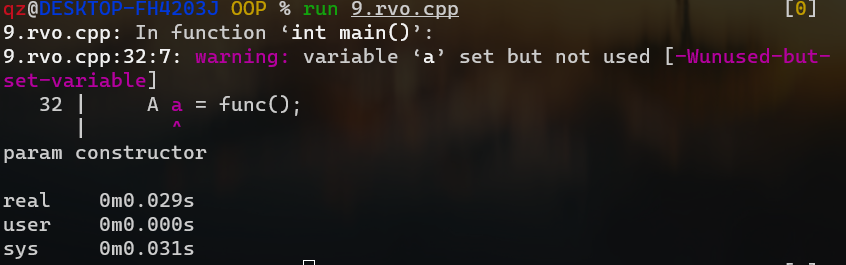
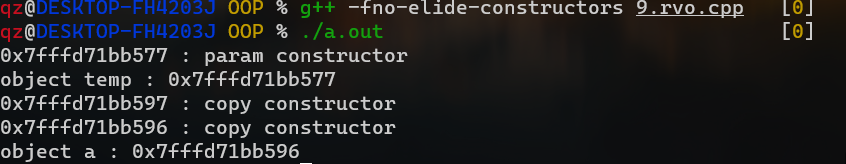
正常情况下会被调用3次构造函数但是输出只调用了一次,而且用的还是有参构造
Step 1:开辟a对象数据区
Step 2∶调用函数func
Step 3:开辟对象temp数据区
Step 4∶调用temp对象的构造函数
Step 5∶使用temp调用a的拷贝构造函数
Step 6∶销毁temp对象、
Step 7∶销毁a对象
取消返回值优化
1 g++ -fno-elide-constructors 9.rvo.cpp
default/delete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class A {public : A() = default ; A(const A &a) = delete ; }; int main () return 0 ; }
源码文件*.cpp 点我跳转:https://github.com/qzwl123/C-/tree/main/%E5%B0%81%E8%A3%85