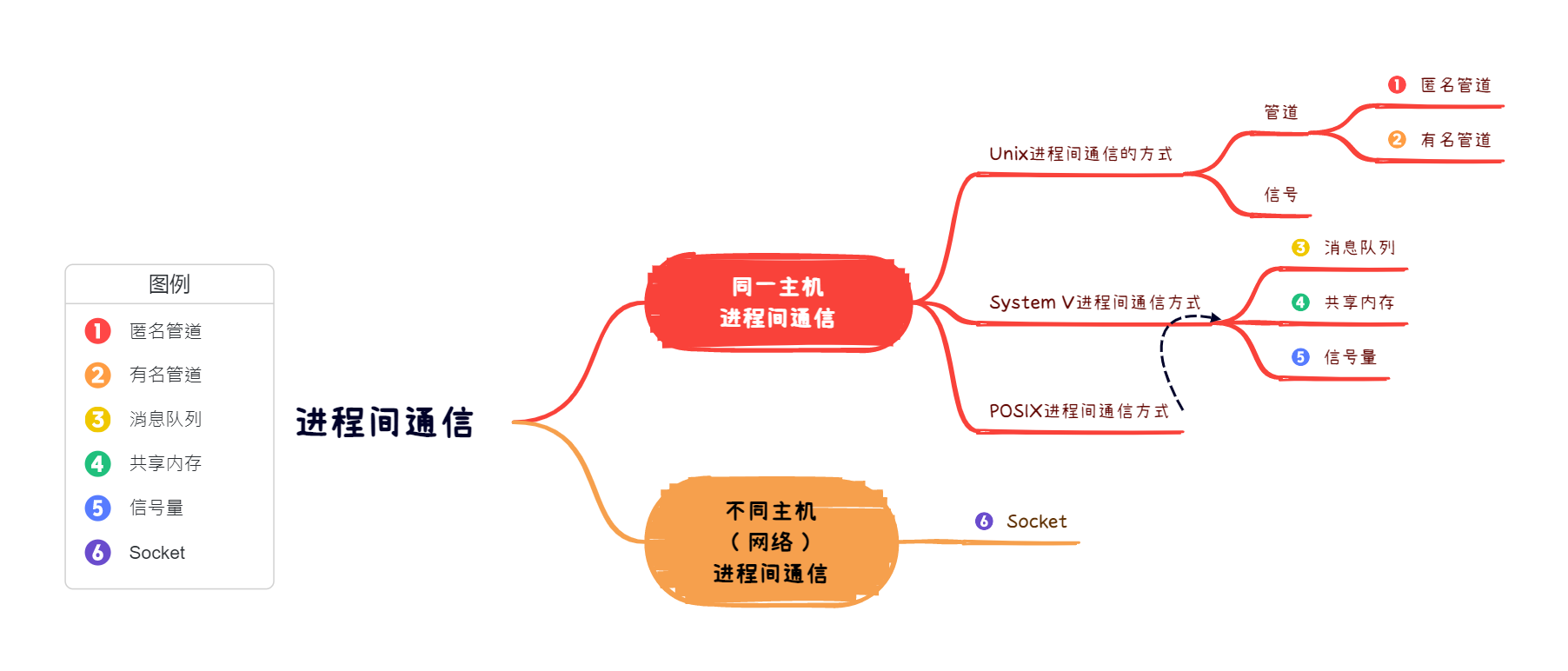
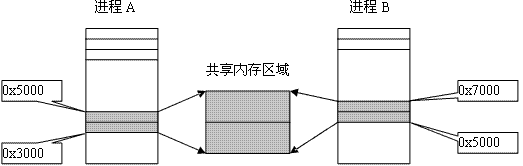
共享内存
共享内存允许两个或者多个进程共享物理内存的同一块区域(通常被称为段)。由于 一个共享内存段会成为一个进程用户空间的一部分,因此这种 IPC 机制无需内核介 入。所有需要做的就是让一个进程将数据复制进共享内存中,并且这部分数据会对其 他所有共享同一个段的进程可用。
与管道等要求发送进程将数据从用户空间的缓冲区复制进内核内存和接收进程将数据 从内核内存复制进用户空间的缓冲区的做法相比,这种 IPC 技术的速度更快
1
2
3
| Linux_Ubuntu(wsl)输入:man shm
shmat shmdt shmop shm_overview
shmctl shmget shm_open shm_unlink
|
共享内存使用步骤
调用 shmget() 创建一个新共享内存段或取得一个既有共享内存段的标识符(即由其 他进程创建的共享内存段)。这个调用将返回后续调用中需要用到的共享内存标识符。
使用 shmat() 来附上共享内存段,即使该段成为调用进程的虚拟内存的一部分。此刻在程序中可以像对待其他可用内存那样对待这个共享内存段。为引用这块共享内存, 程序需要使用由shmat() 调用返回的 addr 值,它是一个指向进程的虚拟地址空间 中该共享内存段的起点的指针。
调用 shmdt() 来分离共享内存段。在这个调用之后,进程就无法再引用这块共享内存 了。这一步是可选的,并且在进程终止时会自动完成这一步。
调用 shmctl() 来删除共享内存段。只有当当前所有附加内存段的进程都与之分离之后内存段才会销毁。只有一个进程需要执行这一步
创建共享内存_函数API简介
shmget 创建共享内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| #include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
- key: 是标识共享内存的键值,可以取非负整数或IPC_PRIVATE
- key_t 类型是一个整形,通过这个找到或者创建一个共享内存, 一般使用16进制表示,非0值
- 当key是IPC_PRIVATE时,shmflg不需要IPC_CREAT。
- 当key是非负整数时,shmflg需要IPC_CREAT。
- size: 是共享内存的大小,以字节为单位。
- shmflg : 是权限标志,与文件的读写权限一样。
- 附加属性: 创建/判断共享内存是不是存在
- 创建: IPC_CREAT
- 判断共享内存是否存在: IPC_EXCL, 需要和IPC_CREAT一起使用
IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664
- 返回值 :
- 成功: 返回 >0 共享内存的引用的ID,后面操作共享内存都是通过这个值
- 失败: 返回 -1 并设置错误
|
shmat 映射共享内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);
- 功能: 和当前的进程进行关联(附加到 shmaddr 指定 shmid上)
- 参数:
- shmid: 共享内存的标识(ID)由shmget返回值获取
- shmaddr:
为NULL: 申请的共享内存的起始地址,指定NULL, 内核指定(系统将选择合适的页面对齐地址以附加段。)
不为NULL : 如果shmaddr不为NULL,并且在SHM_RND中指定了SHM_RNDflg,附加值在最近的shmaddr的地址上。
两者都不是的情况: 否则,shmaddr必须是位于的页面对齐地址(4K)发生连接的位置。
- shmflg: 对共享内存的操作
- 读 : SHM_RDONLY, 必须有读权限
- 读写 : 0
- 返回值:
成功: 返回共享内存的首地址(起始)地址。
失败: (void *) -1
|
shmdt 分离共享内存 本函数调用并不删除所指定的共享内存区,而只是将先前用shmat函数连接(attach)好的共享内 存脱离(detach)目前的进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
- 功能: 解除当前进程和共享内存的关联
- 参数:
shmaddr: 共享内存的首地址
- 返回值:
成功: 0
失败: -1
|
shmctl 控制共享内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
- 功能: 对共享内存进行操作。删除共享内存, 共享内存要删除才会消失, 创建共享内存的进行被销毁了对共享内存是没有任何影响
- 参数:
- shmid: 共享内存的ID
- cmd: 要做的操作
- IPC_STAT:获得共享内存的当前状态
- IPC_SET: 设置共享内存的状态
- IPC_RMID: 标记共享内存被销毁
- buf: 需要设置或者获取的共享内存属性信息
- IPC_STAT:buf存储数据
- IPC_SET: buf中需要初始化数据,设置到内核中
- IPC_RMID: 没有用,NULL
struct shmid_ds {
struct ipc_perm shm_perm;
size_t shm_segsz;
time_t shm_atime;
time_t shm_dtime;
time_t shm_ctime;
pid_t shm_cpid;
pid_t shm_lpid;
shmatt_t shm_nattch;
...
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);
- 功能: 根据指定的路, 和int值,生成一个共享内存的key
- 参数:
- pathname: 指定一个存在的路径
/home/qz/test/
/
- proj_id: int类型的值,但是这关系调用只会使用其中的1个字符
范围: 0 - 255 一般指定一个字符 'a'
|
代码实现_存在bug
需手动关闭内存共享、需要加锁
实现功能 求 1 - 100 累加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define INS 5
struct Num {
int now;
int sum;
};
struct Num *share_memory;
void do_add(int x) {
while(1) {
if(share_memory->now > 100) break;
share_memory->sum += share_memory->now;
share_memory->now++;
printf("<%d> now = %d, sum = %d \n", x, share_memory->now, share_memory->sum);
}
return ;
}
int main() {
pid_t pid;
int x = 0;
int shmid;
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Num), IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
share_memory = (struct Num *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(share_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
share_memory->now = 0;
share_memory->sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
if((pid = fork()) < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
x = i;
if(pid == 0) break;
}
if(pid == 0) {
do_add(x);
} else {
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
wait(NULL);
}
}
printf("share_memory->sum = %d\n", share_memory->sum);
return 0;
}
|
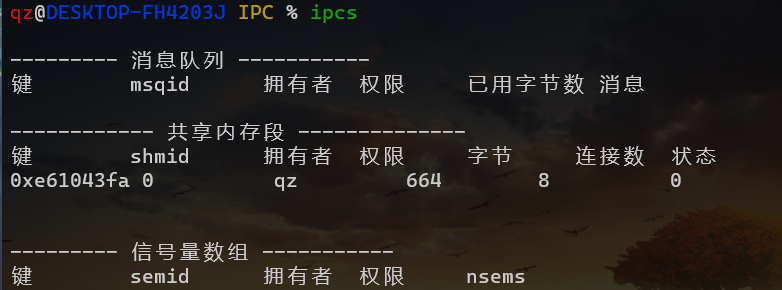
共享内存操作命令
多进程间通信常用的技术手段包括共享内存、消息队列、信号量等等。
ipcs 命令的用途主要用于报告进程间通信设施状态。
shmget: File exists // 提示这个表示共享内存已经存在
但是你发现 ipcs 查看不到 那怎么解决呢? 提权-sudo
sudo ipcs // 再看应该就会有了
1
| ipcrn -m msqid //就可以关闭共享内存
|
| 用法 |
描述 |
| ipcs |
查看帮助: ipcs -help |
| pipcs -a |
// 打印当前系统中所有的进程间通信方式的信息 |
| pipcs -m |
// 打印出使用共享内存进行进程间通信的信息 |
| pipcs -q |
// 打印出使用消息队列进行进程间通信的信息 |
| pipcs -s |
// 打印出使用信号进行进程间通信的信息 |
| ipcrm |
查看帮助: ipcrm-help |
| pipcrm -M |
shmkey // 移除用shmkey创建的共享内存段 |
| pipcrm -m |
shmid // 移除用shmid标识的共享内存段 |
| pipcrm -Q |
msgkey // 移除用msqkey创建的消息队列 |
| pipcrm -q |
msqid // 移除用msqid标识的消息队列 |
| pipcrm -S |
semkey // 移除用semkey创建的信号 |
| pipcrm -s |
semid // 移除用semid标识的信号 |
代码实现_互斥锁
实现了
- 互斥锁
- 共享内存
- ftok()、shmget()、shmat()、shmdt()、shactl().
- 进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define INS 5
struct Num {
int now;
int sum;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
};
struct Num *share_memory;
void do_add(int x) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&share_memory->mutex);
if(share_memory->now > 100) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
break;
}
share_memory->sum += share_memory->now;
share_memory->now++;
printf("<%d> now = %d, sum = %d \n", x, share_memory->now, share_memory->sum);
fflush(stdout);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
}
exit(0);
}
int main() {
pid_t pid;
int x = 0;
int shmid;
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Num), IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
share_memory = (struct Num *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(share_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
share_memory->now = 0;
share_memory->sum = 0;
pthread_mutexattr_t attr;
pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr);
pthread_mutexattr_setpshared(&attr, 1);
pthread_mutex_init(&share_memory->mutex, &attr);
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
if((pid = fork()) < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
x = i;
if(pid == 0) break;
}
if(pid == 0) {
do_add(x);
} else {
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
wait(NULL);
}
}
printf("share_memory->sum = %d\n", share_memory->sum);
shmdt(share_memory);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}
|
代码实现_条件变量
实现了
- 互斥锁 + 条件变量 + 信号
- 共享内存
- ftok()、shmget()、shmat()、shmdt()、shactl().
- 进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define INS 5
struct Num {
int now;
int sum;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
};
struct Num *share_memory;
void do_add(int x) {
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&share_memory->mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&share_memory->cond, &share_memory->mutex);
int flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
if(share_memory->now > 100) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&share_memory->cond);
exit(0);
}
share_memory->sum += share_memory->now;
share_memory->now++;
printf("<%d> now = %d, sum = %d \n", x, share_memory->now, share_memory->sum);
fflush(stdout);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&share_memory->cond);
}
exit(0);
}
int main() {
pid_t pid;
int x = 0;
int shmid;
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Num), IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
share_memory = (struct Num *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(share_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
share_memory->now = 0;
share_memory->sum = 0;
pthread_mutexattr_t attr;
pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr);
pthread_mutexattr_setpshared(&attr, 1);
pthread_mutex_init(&share_memory->mutex, &attr);
pthread_condattr_t c_attr;
pthread_condattr_init(&c_attr);
pthread_condattr_setpshared(&c_attr, 1);
pthread_cond_init(&share_memory->cond, &c_attr);
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
if((pid = fork()) < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
x = i;
if(pid == 0) break;
}
if(pid == 0) {
do_add(x);
} else {
pthread_cond_signal(&share_memory->cond);
for(int i = 1; i <= INS; i++) {
wait(NULL);
}
}
printf("share_memory->sum = %d\n", share_memory->sum);
shmdt(share_memory);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}
|
代码实现_简易进程间通信
head.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#ifndef _HEAD_H
#define _HEAD_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "chat.h"
#endif
|
chat.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#ifndef _CHAT_H
#define _CHAT_H
struct Msg{
char name[20];
char msg[1024];
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
};
#endif
|
server.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
#include "head.h"
struct Msg *shar_memory = NULL;
int main() {
int shmid;
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Msg) ,IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
shar_memory = (struct Msg *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(shar_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
memset(shar_memory, 0, sizeof(struct Msg));
pthread_mutexattr_t m_attr;
pthread_mutexattr_init(&m_attr);
pthread_mutexattr_setpshared(&m_attr, PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED);
pthread_mutex_init(&shar_memory->mutex, &m_attr);
pthread_condattr_t c_attr;
pthread_condattr_init(&c_attr);
pthread_condattr_setpshared(&c_attr, PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED);
pthread_cond_init(&shar_memory->cond, &c_attr);
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&shar_memory->mutex);
printf("Server got the Mutex!\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&shar_memory->cond, &shar_memory->mutex);
printf("Server got the cond signal!\n");
printf("<%s> : %s.\n", shar_memory->name, shar_memory->msg);
memset(shar_memory->msg, 0, sizeof(shar_memory->msg));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shar_memory->mutex);
}
return 0;
}
|
==缺少释放共享内存,解决办法可以使用信号捕捉(CTRL + C)之后再释放共享内存==
client.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
#include "head.h"
struct Msg *share_memory = NULL;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int opt, shmid;
char name[20] = {0};
while((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "n:")) != -1) {
switch(opt) {
case 'n' :
strcpy(name, optarg); break;
default :
fprintf(stderr, "Usage : %s -n name\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
}
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Msg), IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
share_memory = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(share_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
while(1) {
char msg[1024] = {0};
scanf("%[^\n]s", msg);
getchar();
if(!strlen(msg)) continue;
while(1) {
if(!strlen(share_memory->msg)) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&share_memory->mutex);
break;
}
}
printf("Sending : %s... \n", msg);
strcpy(share_memory->msg, msg);
strcpy(share_memory->name, name);
pthread_cond_signal(&share_memory->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
printf("Client signaled the cond\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| /*************************************************************************
> File Name: client.c
> Author: 秃头王
> Mail: 1658339000@qq.com
> Created Time: 2022年10月13日 星期四 10时09分01秒
************************************************************************/
#include "head.h"
struct Msg *share_memory = NULL;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int opt, shmid;
char name[20] = {0};
while((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "n:")) != -1) {
switch(opt) {
case 'n' :
strcpy(name, optarg); break;
default :
fprintf(stderr, "Usage : %s -n name\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
}
key_t key = ftok(".", 2022);
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct Msg), IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0) {
perror("shmget");
exit(1);
}
share_memory = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(share_memory < 0) {
perror("shmat");
exit(1);
}
while(1) {
char msg[1024] = {0};
scanf("%[^\n]s", msg);
getchar();
if(!strlen(msg)) continue;
while(1) {
if(!strlen(share_memory->msg)) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&share_memory->mutex);
break;
}
}
printf("Sending : %s... \n", msg);
strcpy(share_memory->msg, msg);
strcpy(share_memory->name, name);
pthread_cond_signal(&share_memory->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share_memory->mutex);
printf("Client signaled the cond\n");
}
return 0;
}
|













